Here you can find out everything about updates, new features and FAQs.

interactions.
The new features enrich learning and working with the Tactonom Reader with questions and answers. This allows blind people new learning formats that are varied, motivating and fun. And learning success is increased through immediate feedback.
Through “interaction”, the Tactonom Reader becomes an indispensable learning aid, both in the classroom and for homework.
Interactions explained in short
Interactions:
Please also read our detailed PDF instructions on this topic:
This interaction is especially suitable for question-answer applications. In this mode, each question is answered by selecting the correct object. The system gives feedback whether the answer was correct or incorrect.
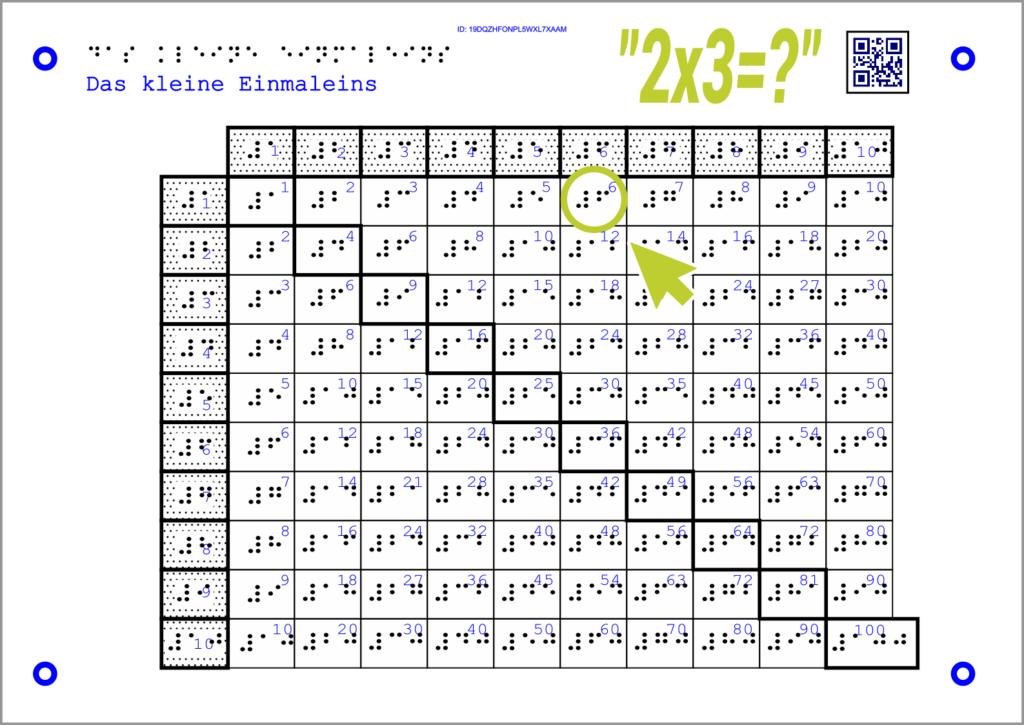
Example math:
The Tactonom Reader asks “What is 2 times 3 ?”.
The answer is given by selecting the result field “6” in the graphic.
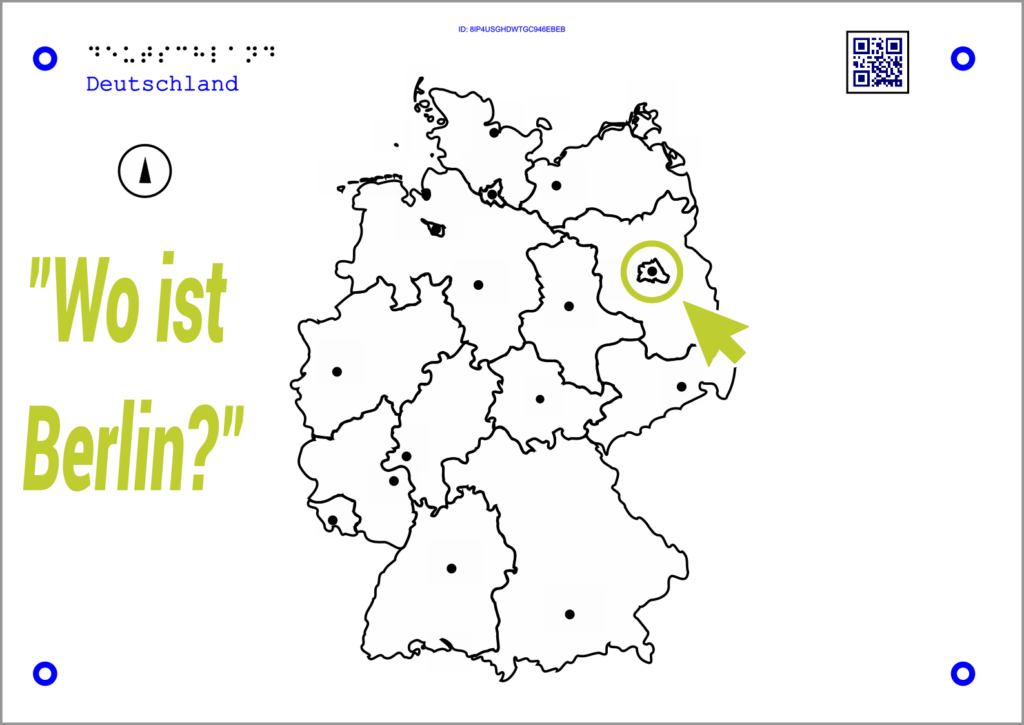
Example geography:
The Tactonom Reader asks: “Where is Berlin?”.
The answer is given by selecting Berlin on the map of Germany.
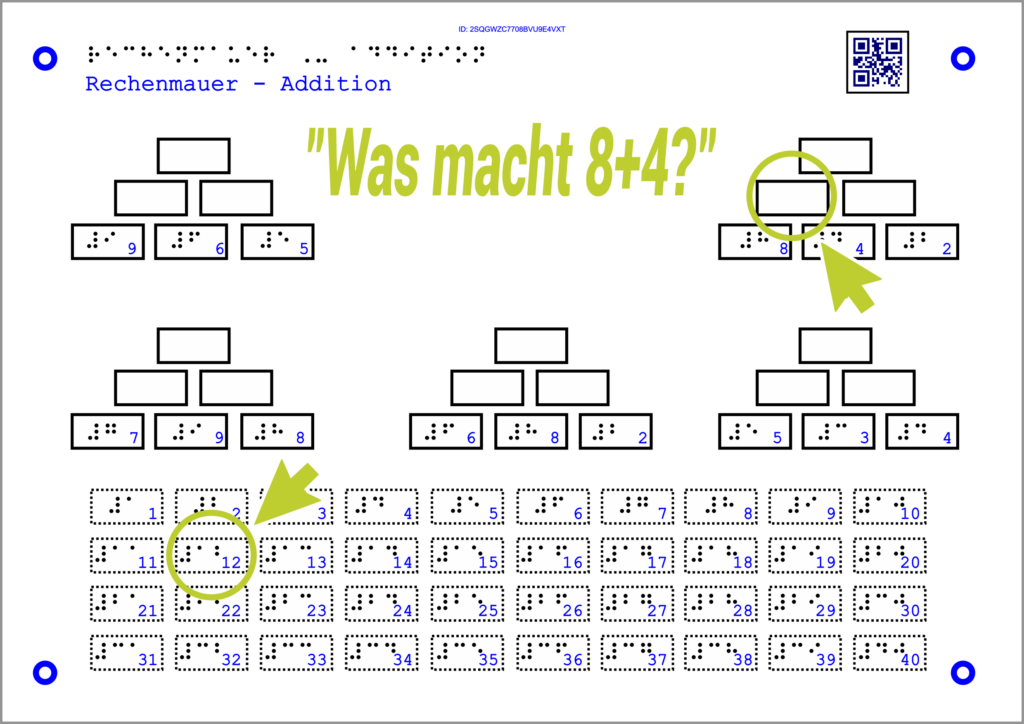
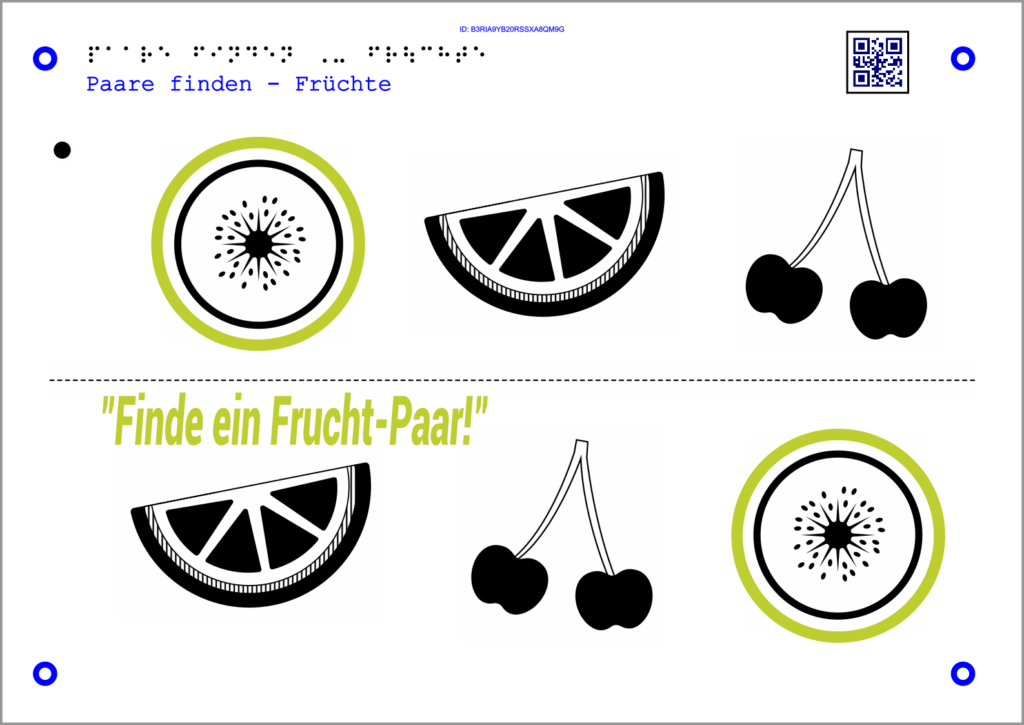
This interaction is particularly suitable for cloze texts and assignments. Two elements that belong together in terms of content are connected by selecting both. The system provides feedback as to whether the answer was correct or incorrect.
Example math:
The Tactonom Reader asks: “What results in 8+4?”.
The answer is given by selecting the field 12.
Example math:
The Tactonom Reader asks:
“Which fruits belong together?”.
The answer is the selection of both fruits that belong together.
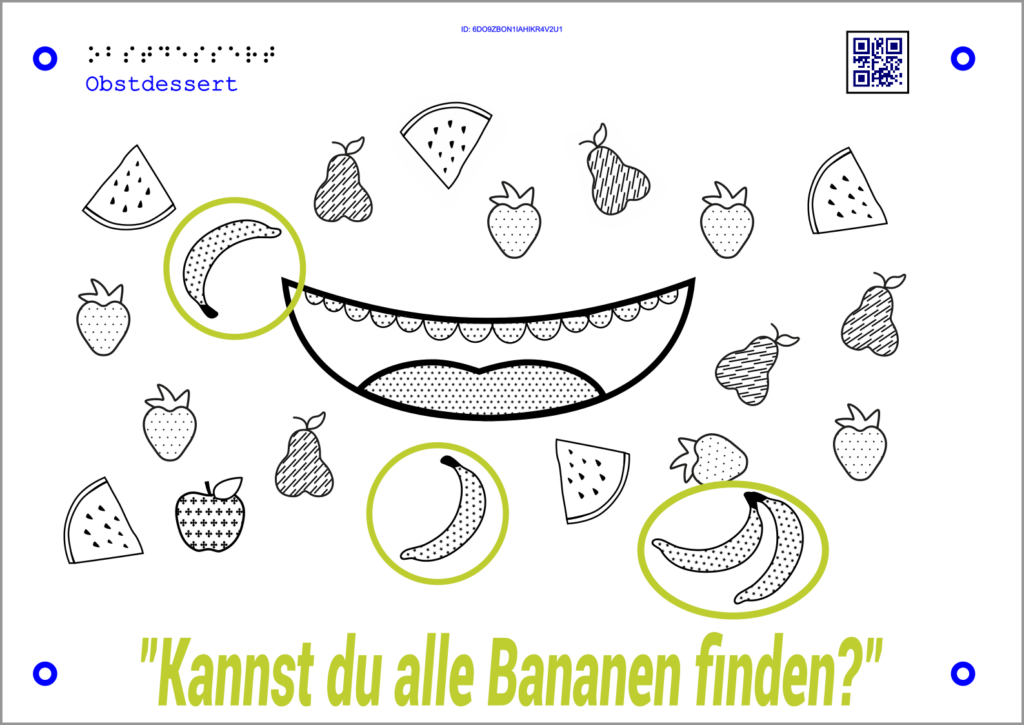
This interaction is particularly suitable for multiple nominations. These can be multiple choice tasks or identifying elements with the same characteristics. The answer consists in selecting all elements that belong together.
Example math:
The Tactonom Reader asks, “Can you find all the bananas?”.
The answer is given by selecting the three bananas shown.

Example math:
The Tactonom Reader asks: “Which numbers can be divided by 5?”.
The answer is given by selecting the four correct fields.
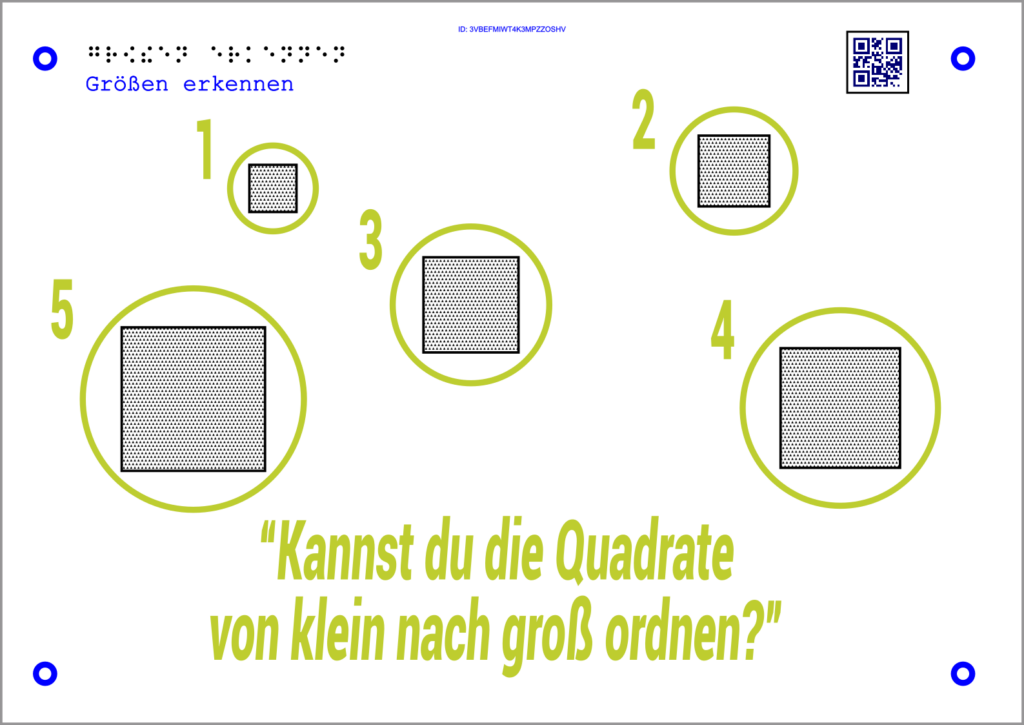
This interaction can be used for sorting, forming ranks and sequences, and guiding the user through a graph.
The answer is given by selecting the elements in the predefined sequence. Here, too, the system reports whether the answer was correct or incorrect in each case.
Example math:
The Tactonom Reader sets the task:
“Sort the squares from small to large!”.
The answer is given by selecting the squares in the correct order.